Menorrhagia: Causes and Treatment of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
If you’ve ever experienced menstrual periods that are so heavy they disrupt your daily life, you might be dealing with menorrhagia. While most women experience varying flow levels during their cycle, heavy periods that last longer than normal can be a sign of an underlying condition. In this blog, we’ll discuss what menorrhagia is, the common causes, and the treatment options available. Let’s dive in and learn how to manage this condition effectively.
What is Menorrhagia?
Menorrhagia, often referred to as heavy menstrual bleeding, is more than just a “bad period.” It’s a condition where a woman’s menstrual flow is abnormally heavy or prolonged, interfering with daily activities and overall well-being. For example, if you find yourself needing to change your sanitary pad or tampon every hour or experiencing periods that last more than seven days, these might be key indicators of menorrhagia.
It’s worth noting that occasional heavy bleeding isn’t always a cause for concern. However, when it happens consistently, it can lead to complications like anemia, fatigue, and even emotional distress. So, understanding the causes and treatment for menorrhagia is essential for your health and peace of mind.

Signs and Symptoms of Menorrhagia
Before diving into the causes, let’s identify some of the common symptoms of menorrhagia. If you recognize these, it’s a good idea to consult your doctor for further evaluation:
- Needing to change your pad or tampon every hour or more frequently.
- Bleeding that lasts longer than 7 days.
- Passing large blood clots during your period.
- Feeling fatigued, weak, or short of breath (possibly due to anemia).
- Waking up at night to change your sanitary product.
- Experiencing heavy menstrual flow that limits daily activities.
These symptoms are not just an inconvenience—they’re a sign that your body may need extra care.
Common Causes of Menorrhagia
Heavy menstrual bleeding doesn’t happen out of nowhere. There are a variety of factors and conditions that can lead to menorrhagia. Below are some of the most common causes:
1. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones like estrogen and progesterone play a vital role in regulating your menstrual cycle. If these hormones are out of balance, your uterine lining (endometrium) can build up excessively, leading to heavier periods. Hormonal imbalances are common during puberty, perimenopause, or in individuals with conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
2. Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids are noncancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding. They are most common in women in their 30s and 40s and can vary in size and number.
3. Polyps
Similar to fibroids, uterine polyps are small growths in the lining of the uterus that can lead to irregular and heavy periods.
4. Adenomyosis
This condition occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. It can cause extremely painful and heavy periods.
5. Bleeding Disorders
Some women have undiagnosed bleeding disorders, such as von Willebrand disease, which can lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding during menstruation.
6. Medications
Certain medications, such as blood thinners or hormonal treatments, can contribute to menorrhagia. If you’ve started a new medication and notice a change in your menstrual flow, consult your doctor.
7. Infections
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or other infections of the reproductive organs can result in abnormal bleeding.
8. Pregnancy Complications
Miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy can lead to heavy bleeding. If you suspect you might be pregnant and experience heavy bleeding, seek medical attention immediately.
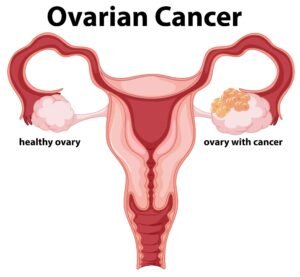
9. Cancer
In rare cases, cancers of the uterus, cervix, or ovaries can cause heavy bleeding. Regular screenings and pap smears are crucial for early detection.
10. IUDs
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) can sometimes cause heavier menstrual bleeding, particularly non-hormonal (copper) IUDs.
Diagnosing Menorrhagia
If you suspect you have menorrhagia, it’s important to seek a diagnosis. Your doctor will likely ask about your menstrual history and may recommend one or more of the following tests:
- Physical Exam: A pelvic exam to check for abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: To identify anemia or clotting disorders.
- Ultrasound: To look for fibroids, polyps, or other uterine abnormalities.
- Biopsy: A sample of uterine tissue may be taken to rule out cancer.
- Sonohysterography or Hysteroscopy: Imaging tests to get a closer look at the uterus.
These diagnostic tools help pinpoint the exact cause of your heavy bleeding so that an effective treatment plan can be developed.
Treatment Options for Menorrhagia
The good news is that menorrhagia can often be managed with the right treatment. The approach will depend on the underlying cause, your overall health, and your personal preferences. Let’s explore some of the most common treatments:
1. Medications
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen can reduce bleeding and relieve menstrual cramps.
- Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, or progesterone pills can regulate your menstrual cycle and reduce bleeding.
- Tranexamic Acid: A prescription medication that helps reduce bleeding during your period.
- Iron Supplements: If anemia is present, iron supplements can help replenish your body’s iron levels.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Sometimes, simple lifestyle adjustments can have a big impact. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and eating a balanced diet can improve hormonal balance and overall health.

3. Minimally Invasive Procedures
For more severe cases of menorrhagia, medical procedures may be recommended:
- Endometrial Ablation: A procedure to remove or destroy the uterine lining, reducing or stopping menstrual flow.
- Hysteroscopy: Used to remove polyps or small fibroids.
- Uterine Artery Embolization: A procedure that shrinks fibroids by cutting off their blood supply.
4. Surgical Options
In extreme cases where other treatments fail, surgery may be necessary:
- Myomectomy: Removal of uterine fibroids while preserving the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus, which eliminates menstruation entirely. This is typically a last resort.
Managing Menorrhagia at Home
While medical treatment is essential, there are steps you can take at home to manage symptoms:
- Keep a period diary to track the frequency and severity of your bleeding.
- Use high-absorbency pads or tampons during heavy flow days.
- Stay hydrated and include iron-rich foods like spinach, red meat, and fortified cereals in your diet.
- Take breaks and rest when needed, especially if you’re feeling fatigued.
When to See a Doctor
If your periods are affecting your quality of life, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Heavy menstrual bleeding can be a sign of a serious condition that needs immediate attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing menorrhagia and maintaining your overall health.

Final Thoughts
Menorrhagia is more common than many people realize, and it’s not something you have to endure in silence. With a better understanding of the causes and treatment options, you can take control of your health and find the relief you deserve. If you suspect you have menorrhagia, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider to explore the best treatment options for you. Remember, your health and well-being always come first.