What Are Some Possible Causes Of Female Infertility?
Infertility is often an emotionally charged and sensitive subject, impacting millions of couples worldwide. If you’re struggling to conceive or supporting someone who is, understanding the causes of female infertility can help ease anxiety and guide you toward possible solutions. While infertility affects both genders equally, this blog specifically addresses the common and lesser-known factors impacting women. Let’s dive in!
What Exactly is Infertility?
Before we discuss the causes of female infertility, it’s important to understand exactly what infertility means. Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after at least one year of actively trying. For women aged 35 and older, infertility is suspected after just six months due to the natural decline in fertility with age.
Now, let’s talk about the primary factors that can impact a woman’s ability to conceive.
Major Causes of Female Infertility
When talking about the causes of female infertility, several factors can come into play. These range from hormonal imbalances and physical abnormalities to lifestyle choices and environmental influences. Here’s a closer look at each category:
1. Ovulation Disorders
Ovulation disorders are among the most common causes of female infertility. They occur when the ovary doesn’t release eggs regularly or fails to release eggs at all. Without ovulation, conception simply cannot occur.
Common ovulation disorders include:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal imbalance affecting around 1 in 10 women of reproductive age. It leads to irregular menstrual cycles and often causes ovulation to stop completely. Women with PCOS often have increased androgen levels, leading to other symptoms like acne, excess hair growth, and weight gain.
- Hypothalamic Dysfunction: When hormones responsible for triggering ovulation are disrupted, ovulation can be erratic or absent. Factors like stress, drastic weight changes, or intense physical activity can contribute to hypothalamic dysfunction.
- Premature Ovarian Failure (POF): Sometimes called primary ovarian insufficiency, POF happens when ovaries stop functioning normally before age 40. This condition significantly reduces fertility.
2. Tubal Infertility
Your fallopian tubes play a crucial role—they’re the pathways that eggs follow to reach the uterus. If these tubes are damaged or blocked, the egg and sperm may not meet, preventing fertilization.
Common reasons for tubal infertility include:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Often caused by sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea, PID can cause permanent scarring in the fallopian tubes.
- Previous surgeries: Any pelvic surgery, especially related to ectopic pregnancies or appendicitis, may leave scars or adhesions that block the fallopian tubes.
- Endometriosis: This common condition causes tissue similar to the uterine lining to grow outside the uterus, often affecting the ovaries and fallopian tubes, making conception difficult.
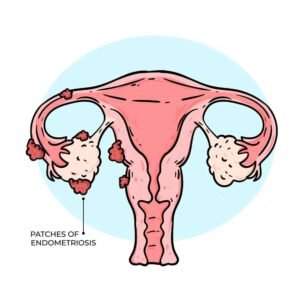
3. Uterine or Cervical Issues
Structural abnormalities in the uterus or cervix can prevent a fertilized egg from implanting successfully. Some common causes of female infertility in this category include:
- Fibroids: Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that can distort the uterine cavity, blocking implantation.
- Endometrial polyps: Polyps are benign growths in the uterus that interfere with implantation or cause miscarriages.
- Congenital uterine abnormalities: Some women are born with uterine shapes that complicate implantation or increase miscarriage risks.
- Cervical stenosis: A narrowed cervical canal may restrict sperm from reaching the egg.
4. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones regulate nearly every aspect of fertility. When there’s an imbalance, conception can become challenging. Key hormonal factors that cause infertility include:
- Thyroid disorders: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism affect ovulation, potentially reducing fertility significantly.
- High prolactin levels: Hyperprolactinemia (high levels of the hormone prolactin) can suppress ovulation, typically caused by stress, medications, or pituitary tumors.
- Insulin resistance: Often seen with conditions like PCOS, insulin resistance can severely disrupt normal ovulation cycles.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors Contributing to Infertility
While biological factors are prominent, several lifestyle and environmental factors also contribute significantly to female infertility:
1. Age
Age is one of the most undeniable causes of female infertility. Fertility naturally decreases as women age, with a significant decline after 35 and even more dramatically after age 40. The quality and quantity of eggs diminish, making pregnancy increasingly difficult.
2. Weight and Nutrition
Being significantly overweight or underweight can impact ovulation. Obesity, for instance, can lead to hormonal imbalances like PCOS or insulin resistance, while underweight women might struggle with irregular cycles due to hormonal disruption. Eating disorders like anorexia can also severely affect fertility.
3. Smoking and Alcohol Use
Regular smoking significantly increases the chances of infertility, primarily by affecting ovarian function and reducing egg quality. Heavy alcohol consumption can similarly decrease fertility, disrupt ovulation, and increase the risk of miscarriage.
4. Stress and Emotional Health
Chronic stress can negatively affect fertility by altering hormone levels and menstrual cycles. Managing stress through mindfulness, therapy, yoga, or meditation can potentially improve fertility outcomes.

5. Exposure to Environmental Toxins
Exposure to pesticides, industrial chemicals, and even certain plastics can disrupt hormone functions, impacting fertility. Reducing exposure to harmful toxins, eating organic when possible, and limiting use of plastics can help improve reproductive health.
Diagnosing the Causes of Female Infertility
If you’re struggling to conceive, it’s essential to consult with a fertility specialist. A thorough fertility evaluation usually includes:
- Ovulation testing to ensure eggs are released regularly.
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG) to check for fallopian tube blockages.
- Ultrasounds and MRI to detect uterine abnormalities.
- Hormone testing for conditions like thyroid disorders and PCOS.
- Laparoscopy for checking conditions such as endometriosis.
Early diagnosis helps your fertility specialist suggest the best treatment options to increase your chances of conceiving.
Treatment Options for Female Infertility
Understanding the causes of female infertility opens the door to potential treatments. Common fertility treatments include:
- Fertility medications: Often prescribed to induce or regulate ovulation.
- Surgical interventions: Surgery may be recommended to clear blockages, remove fibroids, or treat endometriosis.
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI): Placement of sperm directly into the uterus.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): Fertilization of eggs with sperm outside the body, later transferring embryos into the uterus.
Emotional and Mental Health: Coping with Infertility
Infertility is emotionally exhausting, making mental health care equally important. Support groups, counseling, and therapy can provide significant emotional relief during this challenging journey.
Conclusion
Understanding the various causes of female infertility is empowering. It helps women and couples advocate for themselves, seek timely medical intervention, and manage expectations realistically. Remember, infertility is more common than you might think, and medical advancements offer hope to many who dream of parenthood.


